Splunk: Python Lookup
Revision as of 15:31, 14 November 2019 by Rafahsolis (talk | contribs)
Copy requirements to /opt/splunk/lib/python2.7/site-packages
Including splunk_lookup.py:
import csv
import sys
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
class SplunkLookup:
__metaclass__ = ABCMeta
usage = "Usage: python {} [arg1] [arg2]".format(__file__)
def __init__(self):
self.validate_args()
self.arg1, self.arg2 = self.read_arguments()
self.header, self.stdin = self.read_input()
self.writer = self.write_header()
self.process_stdin()
def validate_args(self):
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
print(self.usage)
@staticmethod
def read_arguments():
arg1 = sys.argv[1]
arg2 = sys.argv[2]
return arg1, arg2
@staticmethod
def read_input():
infile = sys.stdin
reader = csv.DictReader(infile)
header = reader.fieldnames
return header, reader
def write_header(self):
stdout = sys.stdout
writer = csv.DictWriter(stdout, fieldnames=self.header)
writer.writeheader()
return writer
def process_stdin(self):
for result in self.stdin:
self.lookup_missing(result)
self.writer.writerow(result)
def lookup_missing(self, result):
if result[self.arg1] and result[self.arg2]:
pass
elif result[self.arg1]:
result.update({self.arg2: self.lookup_arg2(result[self.arg1])})
elif result[self.arg2]:
result.update({self.arg1: self.lookup_arg1(result[self.arg2])})
@abstractmethod
def lookup_arg2(self, argument_value1):
pass
@abstractmethod
def lookup_arg1(self, argument_value2):
pass
class SplunkLookupError(object):
pass
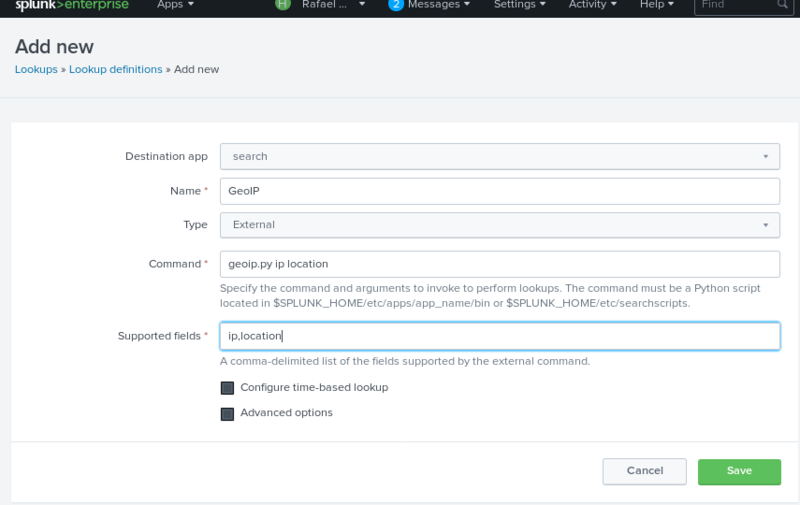
Create your own lookup in: /opt/splunk/etc/system/bin Example : geoip.py
from splunk_lookup import SplunkLookup
from geoip2 import database
DB_PATH = '/usr/share/geoip/GeoIP2-City.mmdb'
class Geolocator(object):
def __init__(self, ip):
self.ip = ip
self.city = self.read_city()
def read_city(self):
reader = database.Reader(DB_PATH)
city = reader.city(self.ip)
reader.close()
return city
@property
def location(self):
return "{city} ({country})".format(city=unknown_if_none(self.city.city.name),
country=unknown_if_none(self.city.country.name))
def unknown_if_none(text):
if text is None:
return 'Unknown'
return text
class SplunkLookupGeoIP(SplunkLookup):
def lookup_arg1(self, argument_value2):
return 'Unknown'
def lookup_arg2(self, argument_value1):
try:
locator = Geolocator(argument_value1)
return locator.location
except Exception as e:
return 'Unknown'
if __name__ == '__main__':
SplunkLookupGeoIP()
Define your lookup At Splunk (Settings > Lookups > Lookup definitions)
Query Usage Example
sourcetype="pfsense:filterlog" host="pfsenseoperacionesinternet.rra.lan" dest_int=pppoe0 direction=inbound vendor_action=block | lookup GeoIP ipaddr as src_ip OUTPUT location | stats count by src_ip, location, dest_port, vendor_action | sort -num(count), sort num(src_ip), sort str(location), sort num(dest_port)